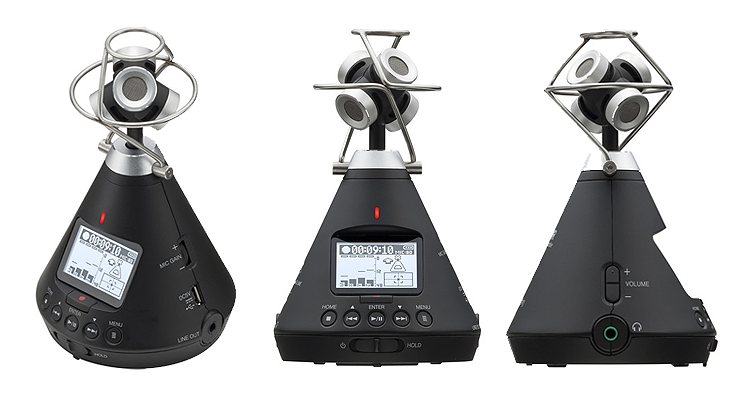
Using two microphones to record a stereo image of a sound source has been around since the beginning of sound recording. Alan Blumlein, an engineer, came up with a method called “binaural recording” in the 1930s. This method used two microphones set up in a figure-8 shape to record a stereo image of a sound source. Later, this method was improved, becoming the basis for how stereo recordings are done today.
“AB microphone” term refers to a specific type of microphone setup that uses two microphones in an “A/B” configuration. The “A” microphone is set up in one place, and the “B” microphone is set up in another. This setup is often used in recording studios or live sound applications to get a more realistic or full-bodied sound by capturing audio from two different angles.
Over the years, the use of AB microphone setups has changed, and now there are many different microphones and ways to use them to make a stereo image of a sound source. The basic idea of using two microphones to get a stereo image is still the same.

Features of an AB Microphone
An AB microphone setup is defined by how the microphones are set up and used, not by what the microphones look like. But when using an AB microphone setup, some things can be helpful:
- Stereo image: An AB microphone setup is often used to make a stereo image of the sound source. This can be done by putting the microphones far enough apart and mixing the sounds from both of them together.
- Frequency response: A microphone’s frequency response is the range of frequencies it can pick up. Some microphones can pick up a wider range of frequencies than others, which can help you record a fuller sound.
- Sensitivity: A microphone‘s sensitivity refers to its ability to pick up sounds. A more sensitive microphone will pick up more sounds, including quieter ones, while a less sensitive microphone will only pick up louder sounds.
- Directionality: A microphone’s directionality is how well it can pick up sounds from different directions. Some microphones are more directional than others, which can help you find the source of a certain sound.
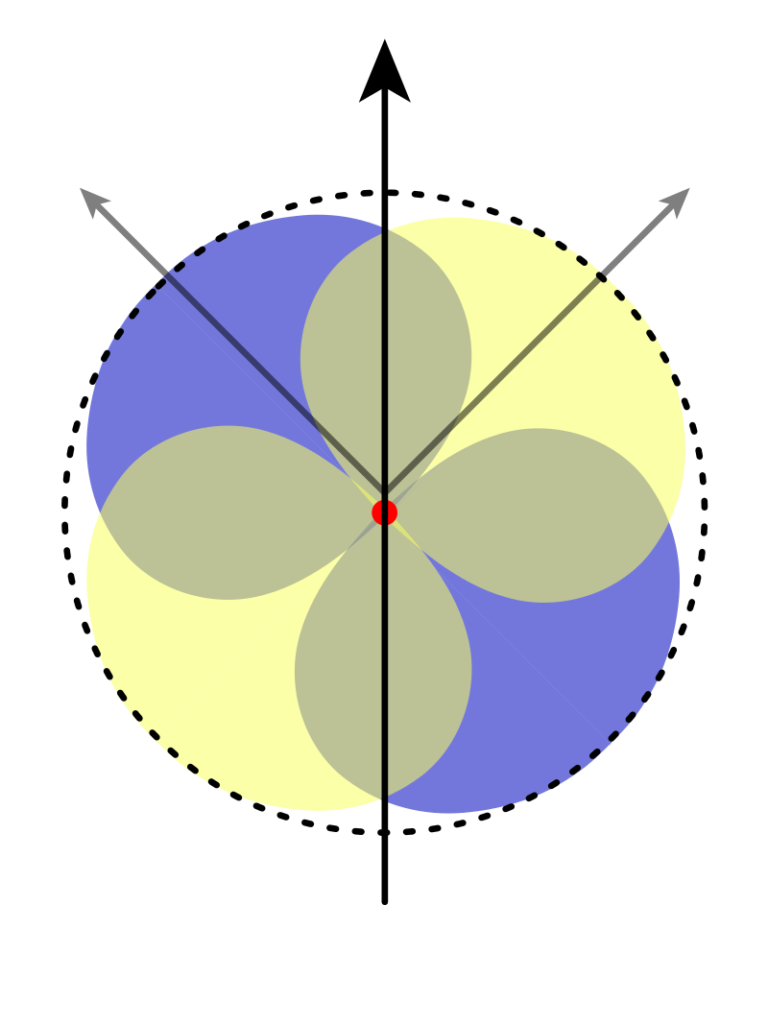
- Polar pattern: A microphone’s polar pattern is the shape of the area around it where it picks up the most sound. Some common polar patterns are the figure-8, the cardioid, and the omnidirectional.
- Compatibility with mixing equipment: It’s important to ensure that the microphones you’re using are compatible with your mixing equipment. This includes the type of connector the microphones use and how much resistance the mixing equipment has when plugged in.
What is AB Microphone?
This method uses two parallel, usually omnidirectional, microphones that are some distance apart. The microphones record time-of-arrival stereo information and some level (amplitude) difference information, especially if they are used close to the sound source (s).
Which stereo microphone technique is also known as AB stereo?
The way to record in A/B stereo is called “Spaced Pair.” It uses two microphones 3 to 10 feet apart and aimed at the same sound source. The distance between them will make the input they get to arrive at different times (phase) and different levels (amplitude).
What is AB in audio?
What is an AB amp?
A Class AB amplifier has the sound quality of a Class A amplifier and the efficiency of a Class B amplifier. This performance is made possible by biassing both transistors to have a signal output close to zero. This is the point where Class B amplifiers start to behave in a nonlinear way (Figure 3).